Ribbon Bar Command: Edit |

|

|
|
Ribbon Bar Command: Edit |

|

|
This command opens a property sheet for defining the mechanism and the thermodynamic/kinetic parameters used by the fitting procedure as starting parameters. The appearance of the individual property pages is identical with that raised by the Edit-command on the Tabbed Window:Simulations. However, when closing the property sheet with OK the Run command is automatically executed and the current curve simulated on the basis of the entered mechanism and parameters is shown in the client area together with the current curve of the active experiment. This enables the user to check how well the experimental current curve can be approximated on the basis of the entered mechanism and starting parameters.
For this purpose the parameters edited on the Property Page:Simulation Parameters will be overwritten by those imported from the active experiment. In other words, when working in the Tabbed Window: Data Fitting the Property Page: Simulation Parameters is mainly provided only for viewing the simulation parameters imported by the active experiment. Only the Level of Multi-Core CPU-support or a modification of parameters belonging to the groups Model Parameters, 2D-Simulation and FEM-Simulation is not reset when closing the property page.
Before the Data Fitting can be started it is essential to select the parameters which are to be optimized by the fitting procedure. This is demonstrated here by means of the example file Fitting.cvd which is installed in DigiElch's home directory. Editing the mechanism and starting parameters in the Property Page: Chemical Reactions looks as follows:
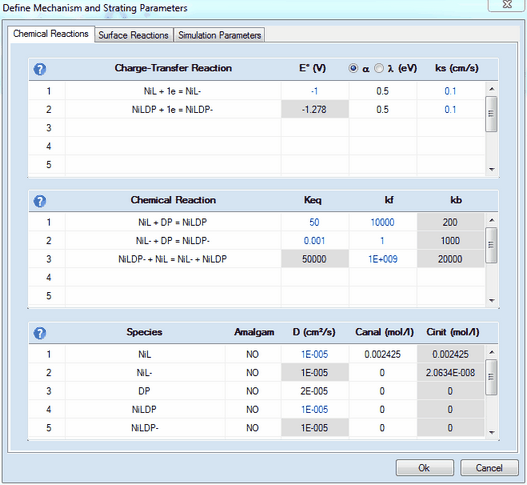
![]() Note that the parameters which are to be optimized by the fitting procedure are plotted in blue. The value of an heterogeneous rate constant, ks, will be plotted in magenta if it is not only selected for being optimized but also linked with the surface coverage of a species.
Note that the parameters which are to be optimized by the fitting procedure are plotted in blue. The value of an heterogeneous rate constant, ks, will be plotted in magenta if it is not only selected for being optimized but also linked with the surface coverage of a species.
Fitting Charge Transfer Parameters
Clicking with the right mouse button on the charge-transfer parameter value which is to be optimized opens the following dialog box
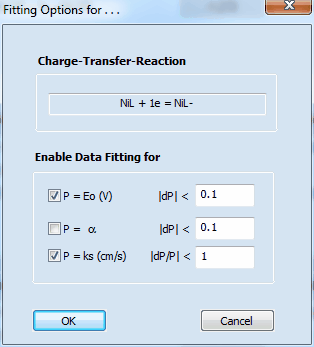
It can be used for selecting/de-selecting the three parameters associated with the underlying charge-transfer reaction for being optimized by the fitting procedure.
In the example on the left hand site, the standard potential, E°(V), and the heterogeneous rate constant, ks (cm/s), associated with the first Charge Transfer Reaction will be optimized. In doing so the change of the standard potential is restricted to 0.1 V per iteration and the relative change of ks remains smaller than the actual parameter value itself in each iteration.
Clicking with the right mouse button on the homogeneous chemical reaction parameter value which is to be optimized opens the following dialog box
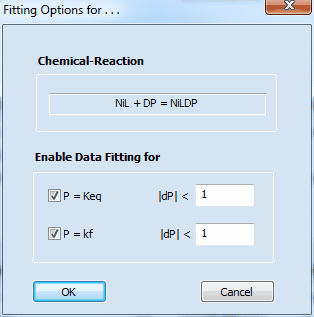
It can be used for selecting/de-selecting the two parameters associated with the underlying chemical reaction for being optimized by the fitting procedure.
In the example on the left hand site, the equilibrium constant, Keq, and the (forward) rate constant, kf, associated with the first Chemical Reaction will be optimized. In doing so the relative change of both remains smaller than the actual parameter values themselves in each iteration.
Fitting the diffusion coefficient of a species
Clicking with the right mouse button on the value of the diffusion coefficient for a particular species opens the following dialog box
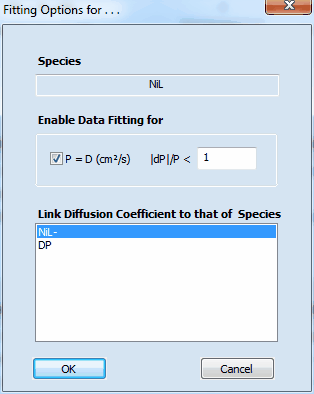
It can be used for selecting/de-selecting the diffusion-coefficient associated with the underlying species for being optimized by the fitting procedure.
The value of |dP|/P defines the maximum relative change of the parameter (diffusion coefficient) value permitted per iteration. In addition, the dialog box provides the option for linking the diffusion coefficients of two or more species. This feature that is very important because of the well-known relationship
E1/2=E° + (RT/nF) ln( DR/DO )
it is impossible to distinguish a shift of the standard potential from the potential shift originating from a ratio DR/DO different from 1. This leads to a perfect parameter coupling that cannot be unraveled mathematically. Consequently, the fitting procedure may not converge if a user is trying to fit the standard potential of a redox couple together with the diffusion coefficients of both species.
Fitting the standard potentials makes sense only if the diffusion coefficients of all species involved in charge transfer reactions are explicitly known or if the ratio DR/DO for each redox couple is forced to remain constant during the data fitting.
In the case of the the example shown above such a linking was done for DNiL/DNiL- = 1 and DNiLDP/DNiLDP- = 1 while DNiLDP and DNiL is optimized (and therefore plotted in blue). Due to the parameter linkage the values of DNiL- and DNiLDP- cannot be modified independently of DNiL and DNiLDP . The input fields associated with linked parameters are therefore blocked as indicated by the grey background color.